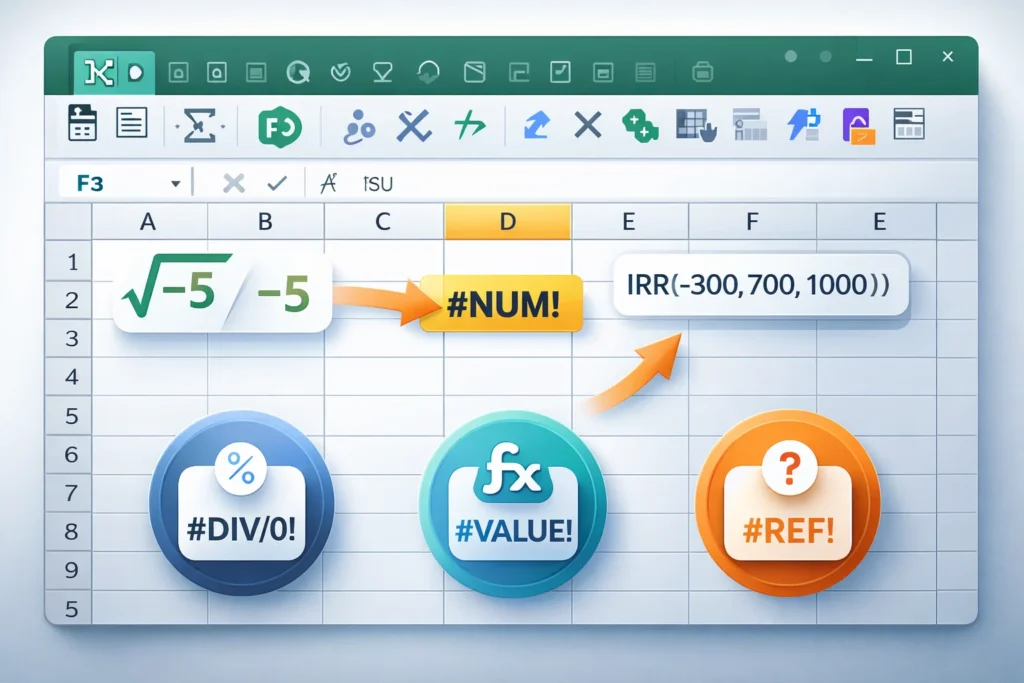
In Excel, “#NUM!” is an error value that appears when a calculation cannot be performed due to invalid numeric operations, such as dividing by zero, taking the square root of a negative number, or exceeding Excel’s numeric limits.
If you’ve ever worked in Excel, you may have seen the dreaded #NUM! error pop up in your spreadsheet. 😬 While it might look intimidating at first, this error is Excel’s way of saying, “There’s a problem with your numbers or formula.”
Understanding what #NUM means in Excel is essential for troubleshooting, preventing data errors, and ensuring your spreadsheets work smoothly. Whether you’re a student, accountant, data analyst, or just a casual Excel user, knowing the causes, examples, and fixes can save you a lot of frustration.
In this article, we’ll explore the meaning of #NUM, common causes, examples, troubleshooting tips, and alternatives. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to handle this error like a pro.
Literal Meaning of “#NUM” in Excel
- #NUM! is an error code, one of several in Excel (like #DIV/0!, #VALUE!, #REF!, etc.)
- Purpose: It indicates invalid numeric operations that Excel cannot calculate.
Key Characteristics
- Always appears with the exclamation mark: #NUM!
- Stops the formula from producing a normal numeric result
- Helps you identify problems with numbers, formulas, or calculations
Common Causes of the #NUM Error
Understanding why #NUM appears is crucial. Here are the most frequent reasons:
1. Invalid Mathematical Operations
- Dividing by zero
- Taking the square root of a negative number
- Logarithms of negative numbers
Example:
=SQRT(-5)
Result: #NUM!
2. Iterative Calculation Issues
Some formulas rely on iterative calculations, like IRR or Goal Seek. If Excel cannot converge to a solution, it shows #NUM.
Example:
=IRR(A1:A5)
Result: #NUM! if Excel can’t find a valid internal rate of return.
3. Exceeding Excel’s Numeric Limits
- Excel has limits on the numbers it can handle (~1E+308 max).
- Extremely large or small numbers in formulas can trigger #NUM.
Example:
=10^500
Result: #NUM!
4. Negative Numbers in Financial Functions
- Some financial functions, like NPV or RATE, may return #NUM! if input values are invalid.
Example:
=RATE(5, -100, 500)
Result: #NUM! if the formula cannot compute a valid rate.
How to Identify #NUM Errors in Your Spreadsheet
Here’s a quick checklist:
| Cause | How to Spot | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Invalid math | Formula references invalid numbers | =SQRT(-10) |
| Iterative calculations | IRR, RATE, or Goal Seek fails | =IRR(A1:A5) |
| Out of bounds numbers | Numbers too large/small | =10^1400 |
| Incorrect financial inputs | Rate or cash flow invalid | =RATE(5, -100, 500) |
💡 Tip: Use the Formula Auditing tool in Excel: Formulas → Error Checking → Trace Error. This helps identify the source of #NUM quickly.
Examples of #NUM Errors in Excel
| Formula | Explanation | Result |
|---|---|---|
=SQRT(-9) | Cannot calculate square root of negative | #NUM! |
=LOG(-10) | Cannot take log of negative number | #NUM! |
=10^500 | Exceeds Excel’s numeric limit | #NUM! |
=IRR(A1:A5) | Iterative calculation cannot converge | #NUM! |
=RATE(5, -100, 500) | Invalid financial inputs | #NUM! |
How to Fix or Avoid #NUM Errors
- Check Your Inputs
- Ensure numbers are valid and appropriate for the function.
- Adjust Iterative Calculations
- Go to File → Options → Formulas → Enable iterative calculation
- Increase Maximum Iterations or Maximum Change for functions like IRR.
- Use IFERROR or IF Functions
- Prevent #NUM from appearing in reports:
=IFERROR(SQRT(A1), "Invalid number") - Break Complex Formulas
- Test parts of your formula individually to find the exact problem.
- Avoid Exceeding Excel Limits
- Use smaller numbers or scale values if possible.
Comparison With Other Excel Errors
| Error | Meaning | Comparison to #NUM! |
|---|---|---|
| #DIV/0! | Dividing by zero | Only occurs with division, not other math errors |
| #VALUE! | Wrong data type | Usually text instead of number |
| #REF! | Invalid cell reference | Reference problem, not calculation |
| #NAME? | Invalid formula name | Formula not recognized |
| #NUM! | Invalid numeric calculation | Specific to numbers and math |
💡 Tip: Understanding the type of error helps you fix it faster.
Polite or Professional Ways to Handle #NUM in Reports
- Use IFERROR to display user-friendly messages instead of #NUM:
=IFERROR(A1/B1, "Calculation not possible")
- Highlight problem cells for review in dashboards or reports
- Document potential causes in spreadsheets for colleagues
FAQ s
- What does #NUM mean in Excel?
It’s an error that appears when a numeric calculation is invalid. - Why do I get #NUM when using SQRT?
SQRT cannot calculate the square root of negative numbers. - Can financial functions cause #NUM?
Yes, functions like IRR or RATE may show #NUM if they can’t converge. - Is #NUM the same as #DIV/0!?
No, #DIV/0! only occurs when dividing by zero. - How can I prevent #NUM errors?
Check input values, use IFERROR, or adjust iterative calculation settings. - Does #NUM mean my data is wrong?
Not always. It usually means Excel cannot compute a numeric result with the given data. - Can #NUM appear in charts?
Yes, if chart data contains #NUM errors, it may not display properly. - Is #NUM fixable?
Yes, by correcting invalid numbers, inputs, or formulas.
Conclusion
The #NUM! error in Excel is a clear signal that something is wrong with your numeric calculations. Whether it’s invalid mathematical operations, financial formulas, or exceeding Excel’s limits, understanding what #NUM means and how to fix it can save you hours of frustration.
By checking inputs, using error-handling functions like IFERROR, and adjusting iterative calculation settings, you can resolve #NUM errors efficiently. Remember, Excel’s error codes are not just obstacles—they’re tools to help you ensure your data is accurate, reliable, and ready for analysis.
Discover More Related Articles:
- Perseverance Mean in the Bible: Lessons from Paul, Job, and Jesus for 2026
- Subdue Meaning in the Bible: Lessons for 2026

Jessica Brown is a language-focused writer who creates well-researched articles on word meanings, abbreviations, and everyday expressions. She contributes to meanvoro.com, delivering simple, reliable, and reader-friendly content designed to make complex terms easy to understand.