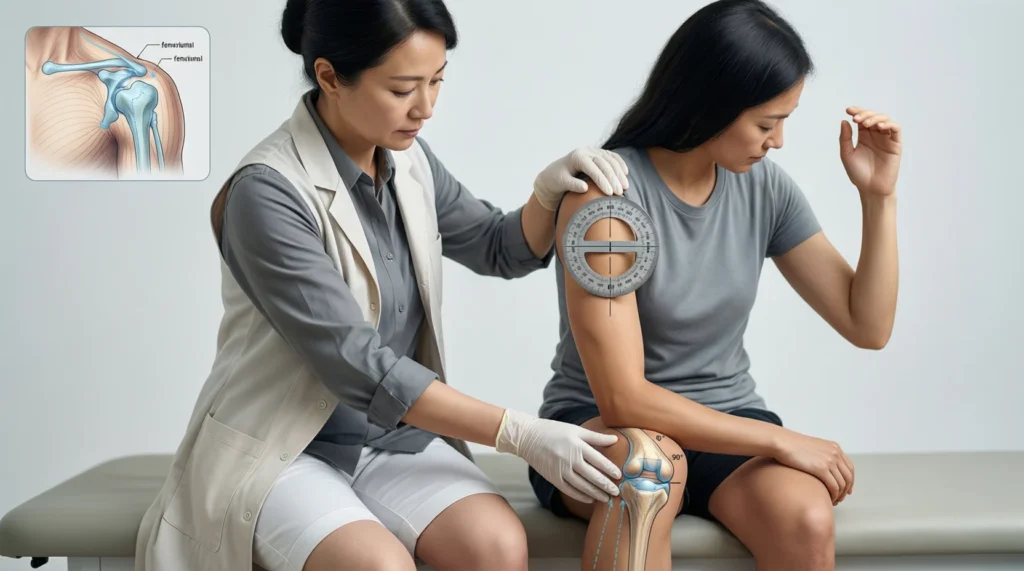
ROM stands for Range of Motion.
It refers to the full movement potential of a joint or body part, usually measured in degrees of a circle or described as full, limited, or restricted.
In short, ROM describes how far and in what directions a joint can move naturally.
If you’ve ever been to a doctor, physical therapist, or read a medical chart, you might have noticed the abbreviation ROM. It appears everywhere in healthcare settings, but it can be confusing if you are not familiar with medical terminology.
Understanding what ROM means in medical terms is essential for patients, caregivers, students, or anyone working in healthcare. It is a simple concept but plays a key role in assessing movement, rehabilitation, and overall health.
This guide explains ROM in detail, with examples, usage tips, and professional context so you can fully understand it.
Why ROM Is Important in Medicine
ROM is crucial because it helps healthcare professionals:
- Assess joint health and flexibility
- Diagnose injuries or conditions
- Plan rehabilitation exercises
- Track progress after surgery, injury, or illness
- Prevent stiffness or mobility loss
Healthcare providers often test ROM during physical exams, physiotherapy sessions, or follow-up appointments.
Origin and Medical Background of ROM
The concept of ROM has existed as long as medical professionals have measured human movement, but it became standardized in modern medicine through physical therapy and orthopedics.
Today, ROM is measured using tools like:
- Goniometers – instruments that measure joint angles
- Inclinometers – devices for spine or large joints
- Observation and manual assessment – common in clinical practice
Types of ROM
ROM is categorized based on how the movement is performed:
1. Active ROM (AROM)
The patient moves the joint by themselves without assistance.
Example:
- Raising your arm above your head during a shoulder test
2. Passive ROM (PROM)
The healthcare provider moves the joint for the patient while the patient remains relaxed.
Example:
- A therapist gently bending your knee after surgery
3. Active-Assisted ROM (AAROM)
A combination where the patient moves the joint with some help from a therapist or device.
Example:
- Using your opposite arm to lift a recovering shoulder
How ROM Is Measured
ROM is typically measured in degrees of a circle, describing the angle a joint moves from start to end.
Common joints measured include:
| Joint | Movement Type | Normal ROM |
|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Flexion | 0–180° |
| Elbow | Flexion | 0–150° |
| Hip | Flexion | 0–120° |
| Knee | Flexion | 0–135° |
| Wrist | Flexion | 0–80° |
These measurements help doctors identify limitations, stiffness, or hypermobility.
Real-Life Examples of ROM in Healthcare
- Physical therapy: A therapist may record shoulder ROM after rotator cuff surgery.
- Orthopedics: A doctor measures knee ROM after a ligament injury.
- Rehabilitation: ROM exercises are prescribed to improve flexibility after stroke or immobilization.
- Sports medicine: Athletes’ joint ROM is assessed to prevent injury or improve performance.
Common Expressions Using ROM
- Limited ROM – The joint cannot move fully
- Full ROM – Normal, unrestricted movement
- ROM exercises – Exercises designed to maintain or improve joint mobility
- ROM assessment – Measuring a joint’s movement potential
Comparison ROM vs Similar Terms
| Term | Meaning | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| ROM | Range of motion | Standard medical term for joint movement |
| Flexibility | Ability of muscles and tissues to stretch | Broader than joint movement alone |
| Mobility | Ability to move independently | Includes strength, coordination, and ROM |
| Goniometry | Measurement of joint angles | A method used to measure ROM |
Polite or Professional Alternatives
When communicating in professional or formal settings, you can replace or expand ROM with:
- Joint range of motion – fully written out
- Articular range of motion – medical, formal term
- Movement assessment – general clinical evaluation
Example:
- Informal: “We need to check ROM.”
- Formal: “We will assess the joint’s range of motion during the examination.”
Alternate Meanings or Confusions
In medicine, ROM always refers to range of motion.
However, outside healthcare, ROM can also mean:
- Read-Only Memory (technology context)
- Return on Margin (finance)
In a medical setting, ROM always refers to joints and movement.
FAQs
Meaning of ROM in medical terms
ROM stands for Range of Motion, describing the movement potential of a joint.
Definition of full ROM
Full ROM means the joint moves normally without restrictions.
Limited ROM explained
Limited ROM occurs when a joint cannot move fully due to injury, stiffness, or pain.
Active ROM description
Active ROM is when the patient moves the joint themselves without assistance.
Passive ROM explained
Passive ROM is when a healthcare provider moves the patient’s joint while the patient stays relaxed.
Why is ROM important
ROM helps assess joint health, plan rehabilitation, and prevent mobility loss.
Can ROM improve with exercises
Yes, physical therapy and ROM exercises can improve flexibility and joint function.
Is ROM used for all joints
Yes, all movable joints, including shoulders, elbows, hips, knees, and wrists, are assessed for ROM.
Practical Tips for Maintaining or Improving ROM
- Perform daily joint exercises after injury or surgery
- Avoid immobilization for long periods
- Include active and passive ROM exercises as recommended by therapists
- Track progress with measurements to see improvements
- Combine ROM exercises with strength and flexibility training
Conclusion
ROM in medical terms is a critical measure of joint health, flexibility, and recovery. Understanding range of motion helps patients and healthcare providers assess injury, track rehabilitation, and improve overall mobility.
By learning about ROM, you can:
- Understand physical therapy instructions
- Monitor your progress after surgery or injury
- Improve your flexibility safely
- Communicate more effectively with healthcare professionals
ROM is a simple abbreviation with a major impact on rehabilitation and daily health.
Discover More Related Articles:
- Biblical Meaning of Defiled: What It Really Means According to Scripture (2026)
- Perseverance Mean in the Bible: Lessons from Paul, Job, and Jesus for 2026

Ryan Thompson is an experienced content writer specializing in slang terms, texting abbreviations, and word meanings. He writes for meanvoro.com, where he creates accurate and easy-to-understand language content for readers.